The retail landscape is undergoing a change unmatched in recent past. This change has brought about a number of challenges for retailers ranging from complex customer behaviour and stiff competition to newer retail channels like e-commerce.
In this complex retail landscape, a single strategy is never enough. Retailers are required to cut through all the noise and reach their customers and capture them by providing a unique & personalized experience.
Leading retailers are creating unprecedented business value & competitive edge by investing heavily in technological advancements. With this Technology-driven Evolution in retail & e-commerce, these companies are constantly listening to what the customers want, how they are reacting to a new product and what the competition is doing.
With all this information these retailers are rightly positioned for the next wave of transformation. This data is fuelling these retailers to formulate an optimum strategy for their business along with monitoring & changing them if required.
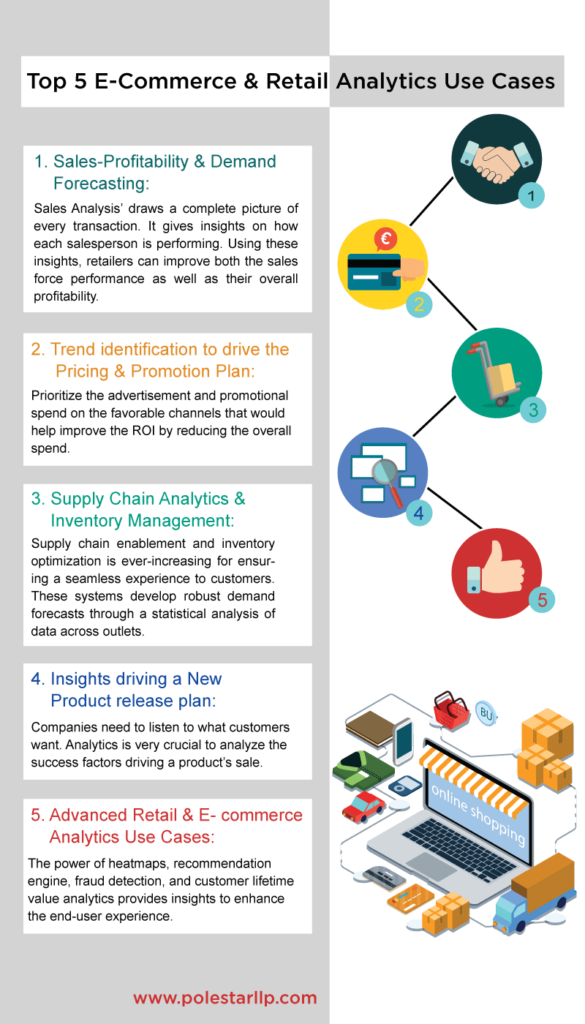
Sales-Profitability & Demand Forecasting
The use of retail analytics to analyze sales performance and optimize processes is very critical for any business. With the help of a Business Intelligence tool, a company can dive deeper into their data, analyze patterns & correlations into their sales data & identify outliers through visually appealing & intuitive dashboards. These tools offer the following use cases pertaining to Sales:
These analytics systems help break the data silos and accumulate all the data in a single place. ‘Sales Analysis’ draws a complete picture of every transaction like mode of purchase, payment details, customer demographics information, discount coupon/promotional offer applied, return queries and refund status.
Sales Personnel Performance & Profitability Analysis gives insights into how each salesperson is performing. A retailer can drill down into these BI dashboards to get insights on area/category/product- wise sales performance, map it with the respective sales personnel & identify profitable opportunities. Using these insights, retailers can improve both the sales force performance as well as their overall profitability.
Losing a sales opportunity because of stock out hurts the company’s sale as well as the buyer’s experience. An analytics system could project sales of different items basis the past trends and minimise the opportunity cost. There are some very comprehensive ‘Demand Forecasting Modules’ adopted by leading retailers. These systems can model scenario analysis to improve the sales goal setting through infusing market data to suggest the latest trends.
It takes into account the effect of seasonality, any executed Ad-campaigns, running Sales Promotion events or any competitor’s activity that can impact sales. These insights help retailers in stocking the inventory accordingly.
Market Basket Analysis uncovers associations between items; it may be because these are complementary products or have a tendency to be bought together. With the help of these insights, the store owners can create a tailored assortment of products and play with the margins by clubbing expensive (high margin) items with less selling discounted items. A correlation between the number of users in a family and identifying cross-sell & up-sell opportunities is key to driving sales.
Identifying customer trends is very crucial for retailers. It requires analysis of a huge set of data, having a robust retail data analytics platform boosts the efficiency in planning and rolling out these promotional activities.
All this has been made possible as the consumers are leaving information through multiple touchpoints before the actual transaction happens. These different touchpoints enable marketers to develop a more detailed customers persona and interpret customers to want. Customer Analytics allows retailers & e-commerce players to push out relevant offers to each customer at every stage of their buyer’s journey.
Retailers can use ‘What-if analysis for costs’ and ‘Analysis of purchase decisions’ to stay relevant in this competitive retail landscape. Use of regression model to understand how store/platform sales correlate with a retail event provides insight into the effectiveness of these events/campaigns.
Price Elasticity Analysis can help retailers develop an understanding of the impact on an item’s sales for per unit change in prices (price elasticity). The low-price elasticity products provide a bundling opportunity with slow-selling high cost (impulse) purchases. These systems ensure that an insight-driven methodology gets adopted while making pricing decisions across the products and the store outlets/websites.
With ‘User Behaviour Analysis’ an e-commerce player can adopt a targeted approach based on user behaviour (number of checkouts as compared to cart abandonment) and preferences (conversion through a well-directed discount on the items in carts).
It favours a more holistic strategy as it not only takes care of sales volume but also enables a check on the sales margin and reduces the customer acquisition cost.
Promotion Channel Analysis can help gain insights on the channels that are working in favour of the retailer. A prioritised advertisement and promotional spend on the favourable channels would help improve the ROI by reducing the overall spend.
The importance of strategic supply chain planning to deal with a crisis/shortage situation is ever-increasing for ensuring a seamless experience for the customers. With omnichannel strategy fuelling retail, an agile supply chain that can deliver products within hours of purchase and nimble reverse supply chains that allow flexible returns is need of the hour. It requires building a trustworthy supplier network.
Much has transformed in the business world, including operational practices, workplace cultures, and financial management technology. Check some of the best practices that organizations use to achieve success.
# Identify the quick wins
Typically, focus your zero-based budgeting initiative either on the larger and more stable business units toiling with profitability or selected overhead areas (such as sales, general, and administrative expenses) where high indirect costs are not clearly understood. Such choices will reinforce the rationale for undertaking ZBB, but they will also deliver the most considerable cost savings with minimal disruption to the rest of the organization.
# Build a culture of alignment and accountability.
As technology enables deeper visibility into what is driving costs and profits, organizations can use zero-based budgeting to align resources and investments more smoothly to strategic goals.
On the one hand, ZBB can shed light on opportunities for more strategic spending that have been overlooked or not considered worthy. According to the Harvard Business Review, one company used ZBB to determine that its commercial discount was higher than it needed to be—an expenditure that wasn’t being reviewed. Another company used ZBB to solve a challenge specific to its logistics costs: labour costs were non-negotiable, but through a ZBB exercise, the company identified a way to reduce costs through negotiations with freight providers.
ZBB also can help to change minds about how spending should be planned. Instead of annual budget planning being a rote process based on traditional spending, each expenditure is scrutinized for what it brings back to the company. The process embeds accountability into decisions.
# Choosing the right planning platform
The success of zero-based budgeting depends on having in-depth insight into the operational drivers of costs like productivity ratios, activity volumes, and input costs—none of which are contained in traditional planning and budgeting software. These older systems only involve highly clustered financial data and, as a consequence, require to be supplemented with substantial amounts of data from elsewhere, such as spreadsheets. Manipulating this data in ancillary spreadsheets increases the workload and complexity involved in any ZBB initiative.
A preferred alternative is to hold all the detailed financial and operational data on a single financial planning and analysis platform like- Anaplan. Such a platform makes it easy to model the causal relationship between activity volumes and the resulting resource needs. Additionally, Anaplan’s proprietary in-memory calculation engine provides the necessary power to process the large volumes of data involved.
With retail analytics systems, retailers/e-commerce decision-makers can create a repeatable framework for Unbiased Vendor Evaluation. For example, the decision-makers can create a vendor evaluation scorecard against some crucial aspects like Cost-Margin, Lead Time, Credit Rating, Distribution Network and other hygiene factors.
The housed Business Intelligence (BI) systems can gauge the Supplier effectiveness vis-a-vis the Key metrics identified by the retailer. It can flag off if inventories from a supplier are failing to meet a specified standard or his return policies are hurting the customer experience in case of e-commerce.
Inventory Optimisation is another use case of Forecasting Systems. These systems develop robust demand forecasts through a statistical analysis of data across outlets. Through these BI systems, a retailer can keep a check on SKUs across outlets. Combining Procurement analytics with supplier effectiveness can help retailers in taking optimum inventory sourcing decision.
These days it’s essential for companies to listen to what customers want. The supply chain is ‘pulled’ by the customer’s demand rather than the traditional ‘push’ strategy driving the trends.
Retailers can use ‘Sentiment Analysis’ to capture this demand and accordingly plan the product pipeline in collaboration with their suppliers. It uses text analytics to draw insights from social media conversations consumers are indulging in.
Analytics is also very crucial to analyse the success factors driving a product’s sale. A benchmarking of these factors could go a long way in building a successful new product strategy. The impact of cannibalization through ‘Scenario Analysis’ is also a very crucial step before a new launch. These modules can help retailers to limit or expedite the investment in a new product launch.
Another very crucial element before a product launch is ‘Competitors’ Analysis’. These Business Analytics tools are capable enough to analyse if a competitor enjoys some unique advantage or has some gap in their product portfolio. Also, a BI system can draw insights from the impact analysis of the competitors’ pricing & promotion events.
Heatmaps: Improve website/store layout: Heatmaps are another very crucial feature of these BI tools. These maps are a lot more visual, which can make them easier to analyse at a glance. These maps draw a gradient on website UI or store layout, the darker spaces represent higher traffic while lighter shades showing lesser traffic.
With the help of these tools, the decision-makers could gauge the behaviour of their existing customers and take optimum business decisions. For example, an e-commerce player can observe what is appealing to his/her customer or from where he/she is bouncing off. What works for a business/product may not work for others. So, e-commerce players can use this information to formulate a standardized strategy for their business.
They can analyze the areas from where users are bouncing off, understand why it is happening (some technical issue or some designing flaws) & most importantly A/B test what is working for them.
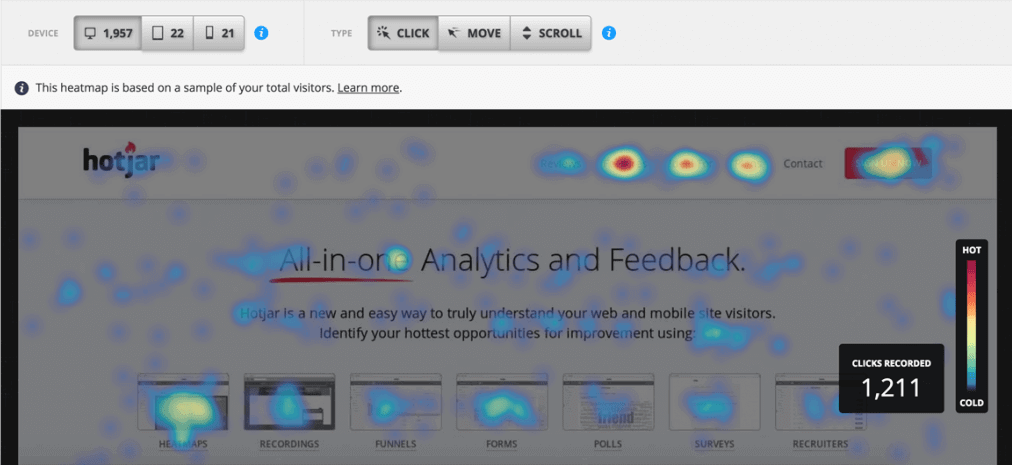
Like website optimization for e-commerce players, a store layout is critical for a brick-mortar store. The store owners never analyse the floor layout critically. They can deploy heatmaps to depict hot and cold zones across the store. This way, they can get a peek into how their customers are exploring their stores. Based on it, they can drive their strategy of assigning shelf space or putting promotional banners accordingly.
Recommendation Engine: Capture the Customer Mind Share Recommendation engines are proving out to be ground-breaking for online sales. These engines are a classic case of machine learning. It observes user behaviour over time and displays ads and promotions to a buyer pertinent to his past explorations.
Fraud Detection: Avoid bad User Experience Deep neural networks find its application in fraud detection. These are highly efficient at not only identifying fraudulent behaviour and flagging it but also in predicting fraud in advance. Incidents like a fraud in return or delivery, the abuse of rights & credit risk significantly harm the retailer’s reputation, predictive neural networks can safeguard against such incidents.
Customer Lifetime Value Analytics: Another crucial aspect for retailers is ‘Customer Lifetime Value’. They often spend a lot on customer acquisition and that customers might churn out. The ‘CLV modules’ consider the user behaviour starting from his first transaction data leading up to the most recent one.
These processes also spot any interdependencies (relevant offers or bad experience) that impact customer behaviour. These models (with data science & machine learning) then suggest to retailers the improvements required in services and priorities related to any customer.
The power of these insights is immense to enhance the end-user experience. Analytics Depot can help you implement these systems is your retail environment (physical as well as digital space). We have developed these capabilities for some big E-commerce & retail clients with our expertise in understanding their problems and deploying suitable analytics systems that enable business decision making.
Subscribe To Our Blogs
Sign up to get the latest news and developments in technology, business analytics, data science and Analytics Depot



